Difference between revisions of "U-Boot on Orange Pi 4"
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[U-Boot]] used on an [[Orange Pi 4]] which sports an [[RK3399]] processor. | [[U-Boot]] used on an [[Orange Pi 4]] which sports an [[RK3399]] processor. | ||
| − | + | This is the first step to getting the device booted and running any software. For the actual OS installation, see [[Linux on Orange Pi 4]]. | |
| + | |||
| + | {{Info|1= | ||
| − | ''' | + | '''Instructions Status''' |
| − | {{Todo| | + | * Compilation on '''x86_64''': ''OK'' |
| + | ** Tried and tested. | ||
| + | * Compilation on '''ARMv8''': ''Partially tested''. | ||
| + | ** Should work with minor tweaks. | ||
| + | ** {{Todo|Finish testing and extend the instructions.}} | ||
| + | }} | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
| Line 11: | Line 18: | ||
See [[U-Boot]] for general concepts and definitions. | See [[U-Boot]] for general concepts and definitions. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[U-Boot]] takes care of the initial booting. It is device (board) specific and so needs to be compiled specifically for [[Orange Pi 4]] as it initializes the hardware, e.g. the RAM modules. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Internally there are 3 (!) bootloaders which form a boot chain: TPL -> SPL -> U-Boot. To boot an actual operating system, U-Boot executes the OS's bootloader, which brings this to 4 (!!) bootloaders in total. Crazy, right? | ||
See [[ARM Trusted Firmware]] for ATF / trust related terminology. | See [[ARM Trusted Firmware]] for ATF / trust related terminology. | ||
| Line 18: | Line 29: | ||
# Loader 1: | # Loader 1: | ||
| − | #* option 1: miniloader | + | #* <span style="color: gray">option 1: miniloader</span> |
#* option 2: SPL/TPL | #* option 2: SPL/TPL | ||
# Loader 2: | # Loader 2: | ||
| − | #* option 1: uboot.img | + | #* <span style="color: gray">option 1: uboot.img</span> |
#* option 2: u-boot.itb | #* option 2: u-boot.itb | ||
# trust.img | # trust.img | ||
| Line 27: | Line 38: | ||
# rootfs.img | # rootfs.img | ||
| − | {{Warning|Option 1 (recommended by [[Rockchip]]) uses closed source tools and binaries | + | {{Warning|Option 1 (recommended by [[Rockchip]]) uses closed source tools and binaries! |
[https://github.com/rockchip-linux/rkbin.git rkbin/tools] are pre-built x86 binaries and are therefore not usable on the target device. The source code is not available for audit or compilation on a different architecture. | [https://github.com/rockchip-linux/rkbin.git rkbin/tools] are pre-built x86 binaries and are therefore not usable on the target device. The source code is not available for audit or compilation on a different architecture. | ||
| − | Therefore this is not a usable route.}} | + | Therefore this is not a usable route and will not be discussed further.}} |
== Setup == | == Setup == | ||
| Line 38: | Line 49: | ||
* dtc (device tree compiler) | * dtc (device tree compiler) | ||
* bc (basic calculator) | * bc (basic calculator) | ||
| − | {{Todo|Not complete}} | + | {{Todo|Not complete. Add packages needed bases on testing on an x86_64 computer.}} |
==== Ubuntu ==== | ==== Ubuntu ==== | ||
| − | {{Todo|Not complete}} | + | {{Todo|Not complete. Add packages needed based on testing on Orange Pi 4.}} |
=== Cross-compilation === | === Cross-compilation === | ||
| Line 49: | Line 60: | ||
=== U-Boot Sources === | === U-Boot Sources === | ||
| − | {{Todo|''orangepi-4-rk3399'' doesn't exist in mainline as of 2020-03-25, [[Applying a git patch|apply this patch]] from [[Armbian]]: [https://github.com/armbian/build/blob/master/patch/u-boot/u-boot-rk3399/add-board-orangepi-4.patch]}} | + | |
| + | '''Note on orangepi-rk3399:''' Though there is an ''orangepi-rk3399'' board available, this is NOT the same as Orange Pi 4. It does have the same processor, but the [[device tree]] is different. Notably there is difference in RAM: DDR3 vs LPDDR4. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Todo|1= | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''orangepi-4-rk3399''' doesn't exist in mainline as of 2020-03-25, [[Applying a git patch|apply this patch]] from [[Armbian]] to add the board definition: [https://github.com/armbian/build/blob/master/patch/u-boot/u-boot-rk3399/add-board-orangepi-4.patch]}} | ||
| + | |||
<pre>git clone https://gitlab.denx.de/u-boot/u-boot.git | <pre>git clone https://gitlab.denx.de/u-boot/u-boot.git | ||
cd u-boot | cd u-boot | ||
make orangepi-4-rk3399_defconfig</pre> | make orangepi-4-rk3399_defconfig</pre> | ||
| − | == Compilation | + | == Compilation == |
=== Export cross compiler for AArch64 === | === Export cross compiler for AArch64 === | ||
Latest revision as of 18:11, 28 March 2020
U-Boot used on an Orange Pi 4 which sports an RK3399 processor.
This is the first step to getting the device booted and running any software. For the actual OS installation, see Linux on Orange Pi 4.
Introduction
See U-Boot for general concepts and definitions.
U-Boot takes care of the initial booting. It is device (board) specific and so needs to be compiled specifically for Orange Pi 4 as it initializes the hardware, e.g. the RAM modules.
Internally there are 3 (!) bootloaders which form a boot chain: TPL -> SPL -> U-Boot. To boot an actual operating system, U-Boot executes the OS's bootloader, which brings this to 4 (!!) bootloaders in total. Crazy, right?
See ARM Trusted Firmware for ATF / trust related terminology.
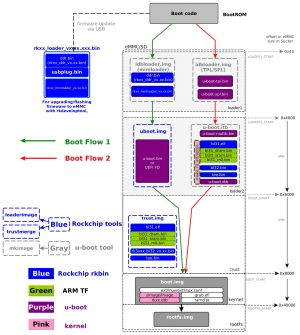
Boot Sequence
Rockchip-specific booting is described here: [3]
- Loader 1:
- option 1: miniloader
- option 2: SPL/TPL
- Loader 2:
- option 1: uboot.img
- option 2: u-boot.itb
- trust.img
- boot.img
- rootfs.img
(!) Option 1 (recommended by Rockchip) uses closed source tools and binaries!
rkbin/tools are pre-built x86 binaries and are therefore not usable on the target device. The source code is not available for audit or compilation on a different architecture.
Therefore this is not a usable route and will not be discussed further.
Setup
Base Build Tools
Arch Linux
- dtc (device tree compiler)
- bc (basic calculator)
TODO: Not complete. Add packages needed bases on testing on an x86_64 computer.
Ubuntu
TODO: Not complete. Add packages needed based on testing on Orange Pi 4.
Cross-compilation
This is needed only if you're not compiling on the Orange Pi 4 (or other ARMv8 device).
- Binaries for aarch64-linux-gnu: [4]
U-Boot Sources
Note on orangepi-rk3399: Though there is an orangepi-rk3399 board available, this is NOT the same as Orange Pi 4. It does have the same processor, but the device tree is different. Notably there is difference in RAM: DDR3 vs LPDDR4.
TODO: orangepi-4-rk3399 doesn't exist in mainline as of 2020-03-25, apply this patch from Armbian to add the board definition: [5]
git clone https://gitlab.denx.de/u-boot/u-boot.git cd u-boot make orangepi-4-rk3399_defconfig
Compilation
Export cross compiler for AArch64
Export cross compiler path for aarch64:
- 'wget' the toolchain binaries (see above)
- 'unxz' the archive
- prepare 'CROSS_COMPILE'
- 'cd gcc-linaro-.../bin'
- 'CROSS_COMPILE_AARCH64=`pwd`'
- 'CROSS_COMPILE=$CROSS_COMPILE_AARCH64'
The usage is this: CROSS_COMPILE=$CROSS_COMPILE (needed only when not running on the target device)
Compile ATF
=> git clone https://github.com/ARM-software/arm-trusted-firmware.git => cd arm-trusted-firmware (export cross compiler path for Cortex-M0 MCU likely arm-none-eabi-) => make realclean => make CROSS_COMPILE=$CROSS_COMPILE PLAT=rk3399 (export bl31.elf) => export BL31=/path/to/arm-trusted-firmware/build/rk3399/release/bl31/bl31.elf
Compile PMU M0 firmware (optional)
TODO: The internally provided cross-compile toolchain for cortex-m0 seems outdated (it wouldn't compile). Skipping for now.
This is optional for most of the rk3399 boards and required only for Puma board.
=> git clone git://git.theobroma-systems.com/rk3399-cortex-m0.git
=> cd rk3399-cortex-m0
(export cross compiler path for Cortex-M0 PMU)
=> make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-cortex_m0-eabi-
(export rk3399m0.bin)
=> export PMUM0=/path/to/rk3399-cortex-m0/rk3399m0.bin
Compile U-Boot
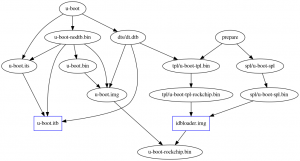
=> cd /path/to/u-boot
=> make orangepi-4-rk3399_defconfig
=> make CROSS_COMPILE=$CROSS_COMPILE
(Get idbloader.img and u-boot.itb)
TODO: The default CONFIG_TARGET_CHROMEBOOK_BOB=y fails to compile. Selecting CONFIG_TARGET_EVG_RK3399=y fixes this and the board successfully loads the bootloader command prompt.
Booting from an SD card
Flashing
Write tpl+spl at 64th sector
sudo dd if=idbloader.img of=/dev/sdc seek=64
Write U-Boot proper at 16384 sector
sudo dd if=u-boot.itb of=/dev/sdc seek=16384 sync
Booting
Put this microSD card into your board and reset it. You should see something like:
U-Boot TPL 2020.04-rc3-00171-g0aadc0786e-dirty (Mar 27 2020 - 00:08:45) Channel 0: LPDDR4, 50MHz BW=32 Col=10 Bk=8 CS0 Row=15 CS1 Row=15 CS=2 Die BW=16 Size=2048MB Channel 1: LPDDR4, 50MHz BW=32 Col=10 Bk=8 CS0 Row=15 CS1 Row=15 CS=2 Die BW=16 Size=2048MB 256B stride 256B stride lpddr4_set_rate: change freq to 400000000 mhz 0, 1 lpddr4_set_rate: change freq to 800000000 mhz 1, 0 Trying to boot from BOOTROM Returning to boot ROM... U-Boot SPL 2020.04-rc3-00171-g0aadc0786e-dirty (Mar 27 2020 - 00:08:45 +0100) Trying to boot from MMC1 U-Boot 2020.04-rc3-00171-g0aadc0786e-dirty (Mar 27 2020 - 00:08:45 +0100) Model: OrangePi 4 AI board DRAM: 3.9 GiB PMIC: RK808 MMC: dwmmc@fe320000: 1, sdhci@fe330000: 0 Loading Environment from MMC... *** Warning - bad CRC, using default environment In: serial@ff1a0000 Out: serial@ff1a0000 Err: serial@ff1a0000 Model: OrangePi 4 AI board Net: eth0: ethernet@fe300000 Hit any key to stop autoboot: 0 =>
Related
External Links
- Main resource: gitlab.denx.de/.../README.rockchip
- Rockchip ATF wiki: [6]
- ATF repository: [7]